DR MANISH-2.pdf laser proctology piles and fistula
0 likes19 views
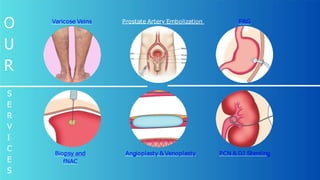
Get the best piles and fistula treatment in Jaipur with advanced laser proctology techniques. Dr. Manish Rajput, a renowned specialist, provides painless, quick, and highly effective treatments for piles, fissures, and fistula. Using cutting-edge laser technology, the procedures ensure minimal discomfort, no stitches, and faster recovery, helping patients return to their daily lives with ease. Dr. Rajput is committed to offering personalized care and long-term solutions, ensuring lasting relief and improved quality of life. With his expertise and modern facilities, you can expect safe and reliable treatment for all proctological conditions.
1 of 6
Download to read offline





Recommended
Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan.... by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 11 views.Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. 



Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan....aeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•11 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan.... by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 13 views.Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. 



Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan....aeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•13 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. Best Deep Vein Thrombosis in Jaipur, Rajasthan by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 6 views. Looking for the best treatment options for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.




Best Deep Vein Thrombosis in Jaipur, Rajasthanaeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•6 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan.... by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 11 views.Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. 



Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan....aeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•11 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan.... by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 11 views.Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. 



Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan....aeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•11 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan.... by aeinjelatechnovation, has 6 slides with 9 views.Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. 



Best DVT doctor in jaipur, Rajasthan....aeinjelatechnovation
6 slides•9 views
Looking for the best treatment options for Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, look no further than the highly esteemed Dr. Manish Rajput. With his extensive expertise and compassionate approach to patient care, Dr. Manish specializes in diagnosing and treating this serious condition.
If you’re searching for the Best DVT Doctor in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput stands out for his exceptional expertise and patient-focused care. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs, potentially leading to life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Dr. Manish Rajput is highly regarded for his advanced understanding of vascular conditions and his ability to provide precise, individualized treatment. Whether it’s medical management through anticoagulant therapy, minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis, or venous stenting, he offers comprehensive solutions tailored to each patient’s needs. Dr. Manish stays updated with the latest advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, ensuring care of the highest international standards. Patients trust his compassionate approach, which emphasizes clear communication, thorough assessment, and long-term management strategies to prevent recurrence. Best Varicose Veins Treatment in Jaipur by deepikavedyan, has 6 slides with 12 views.Varicose veins are enlarged veins near the skin’s surface, often found in the legs due to increased pressure from standing and walking. For Best Varicose Veins Treatment in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput provides advanced, personalized care using modern techniques to help you achieve healthier, smoother legs and a better quality of life.



Best Varicose Veins Treatment in Jaipurdeepikavedyan
6 slides•12 views
Varicose veins are enlarged veins near the skin’s surface, often found in the legs due to increased pressure from standing and walking. For Best Varicose Veins Treatment in Jaipur, Dr. Manish Rajput provides advanced, personalized care using modern techniques to help you achieve healthier, smoother legs and a better quality of life.Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1) by Baburao Bollampalli, has 4 slides with 502 views.This document provides the biographical details of Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO including his education, professional experience, community projects, research, publications, courses attended, organizational activities, and references. It outlines his extensive experience in public health, epidemiology, primary healthcare, teaching, and research in India and abroad.



Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1)Baburao Bollampalli
4 slides•502 views
This document provides the biographical details of Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO including his education, professional experience, community projects, research, publications, courses attended, organizational activities, and references. It outlines his extensive experience in public health, epidemiology, primary healthcare, teaching, and research in India and abroad.CV by Santosh Kumar Bhagat, has 5 slides with 219 views.1. Santosh Kumar Bhagat is a Nepalese radiologist currently working in Yangzhou, China.
2. He has over 10 years of experience as a medical officer and radiologist in Nepal and China.
3. His objective is to grow as a clinical practitioner and researcher by surrounding himself with professionals at the top of their fields.



CVSantosh Kumar Bhagat
5 slides•219 views
1. Santosh Kumar Bhagat is a Nepalese radiologist currently working in Yangzhou, China.
2. He has over 10 years of experience as a medical officer and radiologist in Nepal and China.
3. His objective is to grow as a clinical practitioner and researcher by surrounding himself with professionals at the top of their fields.drakdw (1) by Dr.Ashvini kumar Dwivedi, has 26 slides with 152 views.This document provides biographical information about Dr. A.K. Dwivedi, including his educational background and accomplishments. He has a BHMS, MD in Homeopathy, MBA in HR, and PhD in Schooling. Dr. Dwivedi has had a long career in homeopathy, serving as Chairman of the Board of Studies of Homeopathy at Devi Ahilya University and as a professor. He operates the Advanced Homeo Health Center and Homeopathic Medical Research Center, and publishes a health magazine called Sehat Evam Surat to promote health and homeopathy.



drakdw (1)Dr.Ashvini kumar Dwivedi
26 slides•152 views
This document provides biographical information about Dr. A.K. Dwivedi, including his educational background and accomplishments. He has a BHMS, MD in Homeopathy, MBA in HR, and PhD in Schooling. Dr. Dwivedi has had a long career in homeopathy, serving as Chairman of the Board of Studies of Homeopathy at Devi Ahilya University and as a professor. He operates the Advanced Homeo Health Center and Homeopathic Medical Research Center, and publishes a health magazine called Sehat Evam Surat to promote health and homeopathy.Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1) by Baburao Bollampalli, has 4 slides with 398 views.This document provides details about Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO's education and professional experience. It outlines his medical degrees and fellowships. It then describes his extensive experience working in public health roles in India, including as a professor, health officer, epidemiologist, and gynecologist. It lists the various research projects, surveys, and programs he has been involved in. Finally, it provides references and a list of his scientific research publications.



Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1)Baburao Bollampalli
4 slides•398 views
This document provides details about Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO's education and professional experience. It outlines his medical degrees and fellowships. It then describes his extensive experience working in public health roles in India, including as a professor, health officer, epidemiologist, and gynecologist. It lists the various research projects, surveys, and programs he has been involved in. Finally, it provides references and a list of his scientific research publications.Prof. Mridul M. Panditrao by Prof. Mridul Panditrao, has 13 slides with 482 views.This document provides a detailed summary of Dr. Mridul Panditrao's professional experience and credentials. Over the past 33 years, he has held various roles including Professor, Head of Department, Dean, and Consultant at several hospitals and universities in India, Bahamas, Kuwait, and Jamaica. He has extensive experience in anesthesiology, intensive care, administration, teaching, research, and publishing.



Prof. Mridul M. PanditraoProf. Mridul Panditrao
13 slides•482 views
This document provides a detailed summary of Dr. Mridul Panditrao's professional experience and credentials. Over the past 33 years, he has held various roles including Professor, Head of Department, Dean, and Consultant at several hospitals and universities in India, Bahamas, Kuwait, and Jamaica. He has extensive experience in anesthesiology, intensive care, administration, teaching, research, and publishing.Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1 by International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP), has 5 slides with 319 views.Dr. Ashish Pandey is a qualified dental professional with over 25 years of experience in clinical practice, teaching, and administration. He holds an MDS in Prosthodontics and an MBA in Hospital Administration. Dr. Pandey is currently the Principal, Professor, and Consultant at SDKS Dental College & Hospital in Nagpur, India. He has held various leadership roles, including Vice Principal, at other dental institutions. Dr. Pandey is skilled in prosthodontics, hospital management, teaching, and administration. He seeks an opportunity to utilize his expertise and contribute to organizational objectives through clinical work, research, and teaching.



Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP)
5 slides•319 views
Dr. Ashish Pandey is a qualified dental professional with over 25 years of experience in clinical practice, teaching, and administration. He holds an MDS in Prosthodontics and an MBA in Hospital Administration. Dr. Pandey is currently the Principal, Professor, and Consultant at SDKS Dental College & Hospital in Nagpur, India. He has held various leadership roles, including Vice Principal, at other dental institutions. Dr. Pandey is skilled in prosthodontics, hospital management, teaching, and administration. He seeks an opportunity to utilize his expertise and contribute to organizational objectives through clinical work, research, and teaching.Srikanth resume by jammalamadugu sreekanth, has 4 slides with 114 views.Jammalamadugu Srikanth is seeking an opportunity to utilize his skills as a medical laboratory technologist. He has over 7 years of experience in diagnostic laboratories and has worked in various departments including microbiology, biochemistry, and hematology. He is proficient in collecting samples, operating laboratory machines, analyzing test results, and generating accurate reports. Srikanth holds a D.M.L.T degree from Vaani Institute of Medical Sciences and has worked in several diagnostic centers and hospitals in Andhra Pradesh, India.



Srikanth resumejammalamadugu sreekanth
4 slides•114 views
Jammalamadugu Srikanth is seeking an opportunity to utilize his skills as a medical laboratory technologist. He has over 7 years of experience in diagnostic laboratories and has worked in various departments including microbiology, biochemistry, and hematology. He is proficient in collecting samples, operating laboratory machines, analyzing test results, and generating accurate reports. Srikanth holds a D.M.L.T degree from Vaani Institute of Medical Sciences and has worked in several diagnostic centers and hospitals in Andhra Pradesh, India.Dr. Vishnu Mittal CV by Dr. Vishnu Mittal, has 3 slides with 583 views.Dr. Vishnu Mittal has over 10 years of experience in public health. He received his Masters in Public Health from Panjab University in 2012 and his BDS from Surendra Dental College in 2009. His areas of interest include public health education, health program planning and evaluation, maternal and child health, and research. He has worked as a District Epidemiologist in Haryana and with NGOs and foundations on public health projects. His career objective is to establish a career in public health and contribute to community development and welfare.



Dr. Vishnu Mittal CVDr. Vishnu Mittal
3 slides•583 views
Dr. Vishnu Mittal has over 10 years of experience in public health. He received his Masters in Public Health from Panjab University in 2012 and his BDS from Surendra Dental College in 2009. His areas of interest include public health education, health program planning and evaluation, maternal and child health, and research. He has worked as a District Epidemiologist in Haryana and with NGOs and foundations on public health projects. His career objective is to establish a career in public health and contribute to community development and welfare.RAINBOW INSIGHTS by NARENDRA C MALHOTRA, has 68 slides with 1552 views.The document provides an overview of Rainbow Insights magazine and Rainbow Group of Hospitals. It summarizes the founding and growth of the hospital from the vision of Dr. Prabha Malhotra. The hospital has expanded to provide best services across many medical fields including IVF, neurosurgery, and more. It is dedicated to transparent, high quality patient care with compassion. The document introduces key people involved in leading and managing the hospital.



RAINBOW INSIGHTSNARENDRA C MALHOTRA
68 slides•1.6K views
The document provides an overview of Rainbow Insights magazine and Rainbow Group of Hospitals. It summarizes the founding and growth of the hospital from the vision of Dr. Prabha Malhotra. The hospital has expanded to provide best services across many medical fields including IVF, neurosurgery, and more. It is dedicated to transparent, high quality patient care with compassion. The document introduces key people involved in leading and managing the hospital.zee cv 2014 by zeeshan shaikh, has 14 slides with 445 views.This is a resume for Dr. Jeeshan G. Shaikh, an orthopedic surgeon. He received his medical education in India and obtained a diploma in orthopedics in 2005-2006. His career experience includes positions at various hospitals in Mumbai. His aims are to gain experience at a premier Mumbai institute and learn new orthopedic techniques. He provides contact information for three physician references.



zee cv 2014zeeshan shaikh
14 slides•445 views
This is a resume for Dr. Jeeshan G. Shaikh, an orthopedic surgeon. He received his medical education in India and obtained a diploma in orthopedics in 2005-2006. His career experience includes positions at various hospitals in Mumbai. His aims are to gain experience at a premier Mumbai institute and learn new orthopedic techniques. He provides contact information for three physician references.Ppscmedical medical facilities by kuljyot, has 31 slides with 502 views.The document discusses medical facilities in the Powai region. It describes the main hospitals in the area - Nahar Medical Centre located 1km from the school, and Dr. L. H. Hiranandani Hospital located 4km away. The document includes interviews with doctors at Dr. Hiranandani Hospital about common illnesses, equipment, and nursing facilities. In summary, the document examines the quality and range of healthcare available to residents of the Powai region.



Ppscmedical medical facilitieskuljyot
31 slides•502 views
The document discusses medical facilities in the Powai region. It describes the main hospitals in the area - Nahar Medical Centre located 1km from the school, and Dr. L. H. Hiranandani Hospital located 4km away. The document includes interviews with doctors at Dr. Hiranandani Hospital about common illnesses, equipment, and nursing facilities. In summary, the document examines the quality and range of healthcare available to residents of the Powai region.Textbook of Public Health Dentistry by S. S. Hiremath (z-lib.org).pdf by HubbaAli1, has 522 slides with 1624 views.CD Book, public health dentistry book , hiremath



Textbook of Public Health Dentistry by S. S. Hiremath (z-lib.org).pdfHubbaAli1
522 slides•1.6K views
CD Book, public health dentistry book , hiremathMehta's hospital profile by mehtahospitals, has 3 slides with 107 views.Dr.Mehta's Hospitals Chennai is the best hospital in Chennai with experienced doctors and trained technicians. Dr.Mehta's Hospital s one of the top hospitals in Chennai with 85 years of excellence in the medical field with successful stories of having 5000 and more happy faces cured of severe diseases.



Mehta's hospital profilemehtahospitals
3 slides•107 views
Dr.Mehta's Hospitals Chennai is the best hospital in Chennai with experienced doctors and trained technicians. Dr.Mehta's Hospital s one of the top hospitals in Chennai with 85 years of excellence in the medical field with successful stories of having 5000 and more happy faces cured of severe diseases.Resume dec,2017 by Dr. Bikha Ram Devrajani, has 2 slides with 131 views.Professor Bikha Ram Devrajani is a physician who currently serves as the Vice Chancellor of Liaquat University of Medical and Health Sciences in Jamshoro, Pakistan. He has over 28 years of clinical and teaching experience and holds medical degrees from Pakistan, the United States, and the United Kingdom. Throughout his career, Professor Devrajani has held numerous leadership roles, published over 100 research papers, and received several awards for his contributions to medicine and education.



Resume dec,2017Dr. Bikha Ram Devrajani
2 slides•131 views
Professor Bikha Ram Devrajani is a physician who currently serves as the Vice Chancellor of Liaquat University of Medical and Health Sciences in Jamshoro, Pakistan. He has over 28 years of clinical and teaching experience and holds medical degrees from Pakistan, the United States, and the United Kingdom. Throughout his career, Professor Devrajani has held numerous leadership roles, published over 100 research papers, and received several awards for his contributions to medicine and education.Fogsi focus adbhut matrutva by NARENDRA C MALHOTRA, has 161 slides with 452 views.This document discusses the launch of the "Adbhut Matrutva" project by the Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI) at the All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology on January 19th, 2018. The Adbhut Matrutva program aims to provide holistic antenatal care to reduce maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality as well as prevent noncommunicable diseases. It addresses the fetal origins of adult diseases. The document notes that the Indian government prioritizes healthcare, especially for mothers and children, through programs targeting maternal mortality, infant mortality and malnutrition.



Fogsi focus adbhut matrutvaNARENDRA C MALHOTRA
161 slides•452 views
This document discusses the launch of the "Adbhut Matrutva" project by the Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI) at the All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology on January 19th, 2018. The Adbhut Matrutva program aims to provide holistic antenatal care to reduce maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality as well as prevent noncommunicable diseases. It addresses the fetal origins of adult diseases. The document notes that the Indian government prioritizes healthcare, especially for mothers and children, through programs targeting maternal mortality, infant mortality and malnutrition.Nivedya_resume by Nivedya Amith, has 2 slides with 77 views.Dr. Nivedya D. Ramesh is a homoeopathic physician with over 2 years of experience working in multiple hospitals and clinics. She has skills in identifying patient issues, clinical examination, forming diagnoses, and prescribing homeopathic medicines. Dr. Ramesh completed her BHMS degree from Fr Muller Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital, including a 1-year internship working in 17 different medical facilities. She also has a background in psychology, having worked with cases of ADHD, depression, anxiety and stress disorders. Dr. Ramesh received several academic awards and honors during her education.



Nivedya_resumeNivedya Amith
2 slides•77 views
Dr. Nivedya D. Ramesh is a homoeopathic physician with over 2 years of experience working in multiple hospitals and clinics. She has skills in identifying patient issues, clinical examination, forming diagnoses, and prescribing homeopathic medicines. Dr. Ramesh completed her BHMS degree from Fr Muller Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital, including a 1-year internship working in 17 different medical facilities. She also has a background in psychology, having worked with cases of ADHD, depression, anxiety and stress disorders. Dr. Ramesh received several academic awards and honors during her education.resume by hafiz Ishfaq, has 16 slides with 132 views.This document contains a resume for Hafiz Muhammad Ishfaq. Some key points:
- Ishfaq is an Occupational Therapist and Senior Lecturer currently working at Helping Hands Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences in Mansehra.
- He has a B.S. in Occupational Therapy and a Master's in Public Health.
- Ishfaq has work experience in rehabilitation centers including the Pakistan Society for the Rehabilitation of Disabled in Lahore.
- He has professional certificates in areas like wrist/hand therapy and sensory integration therapy.



resumehafiz Ishfaq
16 slides•132 views
This document contains a resume for Hafiz Muhammad Ishfaq. Some key points:
- Ishfaq is an Occupational Therapist and Senior Lecturer currently working at Helping Hands Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences in Mansehra.
- He has a B.S. in Occupational Therapy and a Master's in Public Health.
- Ishfaq has work experience in rehabilitation centers including the Pakistan Society for the Rehabilitation of Disabled in Lahore.
- He has professional certificates in areas like wrist/hand therapy and sensory integration therapy.India's best of 5 recommended hospital by Merry D'souza, has 36 slides with 90 views.These hospitals are a ray of hope for those ailing patients, who want a relief from their sufferings. Hence, in this issue of Insights Success, we present to you India’s Best of 5 Recommended Hospitals, that are changing the face of healthcare through their dedication and innovation. We also recommend you read articles curated by our in-house editorial team. 



India's best of 5 recommended hospitalMerry D'souza
36 slides•90 views
These hospitals are a ray of hope for those ailing patients, who want a relief from their sufferings. Hence, in this issue of Insights Success, we present to you India’s Best of 5 Recommended Hospitals, that are changing the face of healthcare through their dedication and innovation. We also recommend you read articles curated by our in-house editorial team. CV by Rajashekar SomanattI, has 6 slides with 424 views.Dr. Rajashekar Somanatti is seeking a position in the healthcare industry. He has an MBA from the University of Northampton UK and a BDS from SDM College of Dental Sciences and Hospital. He has over 10 years of experience as a dentist and over 8 years of experience managing clinical services as an administrator at KLES Hospital. He is trained in quality management systems and risk reduction practices.



CVRajashekar SomanattI
6 slides•424 views
Dr. Rajashekar Somanatti is seeking a position in the healthcare industry. He has an MBA from the University of Northampton UK and a BDS from SDM College of Dental Sciences and Hospital. He has over 10 years of experience as a dentist and over 8 years of experience managing clinical services as an administrator at KLES Hospital. He is trained in quality management systems and risk reduction practices.Detailed report on Ramesh Hospital IN GUNTUR by madhuvenkatasainath yangalasetty, has 40 slides with 2662 views.THIS MY DETAILED REPORT ON RAMESH HOSPIAL. IN THE SUMMER INTERNSHIP TIME. IN THIS REPORT WHAT ARE AVAILABLE IN HOPITAL AND MY WORK . MY WORK WAS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ABOUT THE RAMESH HOSPITAL.



Detailed report on Ramesh Hospital IN GUNTURmadhuvenkatasainath yangalasetty
40 slides•2.7K views
THIS MY DETAILED REPORT ON RAMESH HOSPIAL. IN THE SUMMER INTERNSHIP TIME. IN THIS REPORT WHAT ARE AVAILABLE IN HOPITAL AND MY WORK . MY WORK WAS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ABOUT THE RAMESH HOSPITAL.Cv -amit by Global Oral Health Foundation Society, has 3 slides with 78 views.Dr. Amit Saini is a dental surgeon looking to work with non-profits on oral health initiatives for underserved rural communities. He operates his own dental clinic in Nawanshahr, India and has over 20 years of experience in dentistry. He also started his own NGO called the Global Oral Health Foundation Society to provide affordable dental care to rural and marginalized groups.



Cv -amitGlobal Oral Health Foundation Society
3 slides•78 views
Dr. Amit Saini is a dental surgeon looking to work with non-profits on oral health initiatives for underserved rural communities. He operates his own dental clinic in Nawanshahr, India and has over 20 years of experience in dentistry. He also started his own NGO called the Global Oral Health Foundation Society to provide affordable dental care to rural and marginalized groups.newer Drug Delivery system by Dr Shraddha pharmacology.pptx by Dr Shraddha Mishra, has 65 slides with 57 views.novel drug delivery system , newer drug delivery system by dr shraddha mishra mbbs md pharmacology 



newer Drug Delivery system by Dr Shraddha pharmacology.pptxDr Shraddha Mishra
65 slides•57 views
novel drug delivery system , newer drug delivery system by dr shraddha mishra mbbs md pharmacology Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination by Suyash Jain, has 19 slides with 162 views.Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination
introduction about ranitidine
rise and fall of ranitidine:- drug discovery pipeline
NDMA Contamination: A Ticking Time Bomb
VALISURA laboratory
Claims by VALISURA
Testing Methods for NDMA
Regulatory Procedure Timeline
European Medical Agency
CHMP(Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use)
usfda
Recall
what are recalls
21CFR
Recall Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Regulatory actions
(FDA recall, EMA recommendations)
Guidelines to consumers
Alternatives to ranitidine
What Ranitidine Taught Us About Drug Safety?




Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA ContaminationSuyash Jain
19 slides•162 views
Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination
introduction about ranitidine
rise and fall of ranitidine:- drug discovery pipeline
NDMA Contamination: A Ticking Time Bomb
VALISURA laboratory
Claims by VALISURA
Testing Methods for NDMA
Regulatory Procedure Timeline
European Medical Agency
CHMP(Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use)
usfda
Recall
what are recalls
21CFR
Recall Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Regulatory actions
(FDA recall, EMA recommendations)
Guidelines to consumers
Alternatives to ranitidine
What Ranitidine Taught Us About Drug Safety?
More Related Content
Similar to DR MANISH-2.pdf laser proctology piles and fistula (20)
CV by Santosh Kumar Bhagat, has 5 slides with 219 views.1. Santosh Kumar Bhagat is a Nepalese radiologist currently working in Yangzhou, China.
2. He has over 10 years of experience as a medical officer and radiologist in Nepal and China.
3. His objective is to grow as a clinical practitioner and researcher by surrounding himself with professionals at the top of their fields.



CVSantosh Kumar Bhagat
5 slides•219 views
1. Santosh Kumar Bhagat is a Nepalese radiologist currently working in Yangzhou, China.
2. He has over 10 years of experience as a medical officer and radiologist in Nepal and China.
3. His objective is to grow as a clinical practitioner and researcher by surrounding himself with professionals at the top of their fields.drakdw (1) by Dr.Ashvini kumar Dwivedi, has 26 slides with 152 views.This document provides biographical information about Dr. A.K. Dwivedi, including his educational background and accomplishments. He has a BHMS, MD in Homeopathy, MBA in HR, and PhD in Schooling. Dr. Dwivedi has had a long career in homeopathy, serving as Chairman of the Board of Studies of Homeopathy at Devi Ahilya University and as a professor. He operates the Advanced Homeo Health Center and Homeopathic Medical Research Center, and publishes a health magazine called Sehat Evam Surat to promote health and homeopathy.



drakdw (1)Dr.Ashvini kumar Dwivedi
26 slides•152 views
This document provides biographical information about Dr. A.K. Dwivedi, including his educational background and accomplishments. He has a BHMS, MD in Homeopathy, MBA in HR, and PhD in Schooling. Dr. Dwivedi has had a long career in homeopathy, serving as Chairman of the Board of Studies of Homeopathy at Devi Ahilya University and as a professor. He operates the Advanced Homeo Health Center and Homeopathic Medical Research Center, and publishes a health magazine called Sehat Evam Surat to promote health and homeopathy.Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1) by Baburao Bollampalli, has 4 slides with 398 views.This document provides details about Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO's education and professional experience. It outlines his medical degrees and fellowships. It then describes his extensive experience working in public health roles in India, including as a professor, health officer, epidemiologist, and gynecologist. It lists the various research projects, surveys, and programs he has been involved in. Finally, it provides references and a list of his scientific research publications.



Babu Rao Bollampalli CV New US (1) (1)Baburao Bollampalli
4 slides•398 views
This document provides details about Dr. BOLLAMPALLI BABU RAO's education and professional experience. It outlines his medical degrees and fellowships. It then describes his extensive experience working in public health roles in India, including as a professor, health officer, epidemiologist, and gynecologist. It lists the various research projects, surveys, and programs he has been involved in. Finally, it provides references and a list of his scientific research publications.Prof. Mridul M. Panditrao by Prof. Mridul Panditrao, has 13 slides with 482 views.This document provides a detailed summary of Dr. Mridul Panditrao's professional experience and credentials. Over the past 33 years, he has held various roles including Professor, Head of Department, Dean, and Consultant at several hospitals and universities in India, Bahamas, Kuwait, and Jamaica. He has extensive experience in anesthesiology, intensive care, administration, teaching, research, and publishing.



Prof. Mridul M. PanditraoProf. Mridul Panditrao
13 slides•482 views
This document provides a detailed summary of Dr. Mridul Panditrao's professional experience and credentials. Over the past 33 years, he has held various roles including Professor, Head of Department, Dean, and Consultant at several hospitals and universities in India, Bahamas, Kuwait, and Jamaica. He has extensive experience in anesthesiology, intensive care, administration, teaching, research, and publishing.Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1 by International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP), has 5 slides with 319 views.Dr. Ashish Pandey is a qualified dental professional with over 25 years of experience in clinical practice, teaching, and administration. He holds an MDS in Prosthodontics and an MBA in Hospital Administration. Dr. Pandey is currently the Principal, Professor, and Consultant at SDKS Dental College & Hospital in Nagpur, India. He has held various leadership roles, including Vice Principal, at other dental institutions. Dr. Pandey is skilled in prosthodontics, hospital management, teaching, and administration. He seeks an opportunity to utilize his expertise and contribute to organizational objectives through clinical work, research, and teaching.



Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP)
5 slides•319 views
Dr. Ashish Pandey is a qualified dental professional with over 25 years of experience in clinical practice, teaching, and administration. He holds an MDS in Prosthodontics and an MBA in Hospital Administration. Dr. Pandey is currently the Principal, Professor, and Consultant at SDKS Dental College & Hospital in Nagpur, India. He has held various leadership roles, including Vice Principal, at other dental institutions. Dr. Pandey is skilled in prosthodontics, hospital management, teaching, and administration. He seeks an opportunity to utilize his expertise and contribute to organizational objectives through clinical work, research, and teaching.Srikanth resume by jammalamadugu sreekanth, has 4 slides with 114 views.Jammalamadugu Srikanth is seeking an opportunity to utilize his skills as a medical laboratory technologist. He has over 7 years of experience in diagnostic laboratories and has worked in various departments including microbiology, biochemistry, and hematology. He is proficient in collecting samples, operating laboratory machines, analyzing test results, and generating accurate reports. Srikanth holds a D.M.L.T degree from Vaani Institute of Medical Sciences and has worked in several diagnostic centers and hospitals in Andhra Pradesh, India.



Srikanth resumejammalamadugu sreekanth
4 slides•114 views
Jammalamadugu Srikanth is seeking an opportunity to utilize his skills as a medical laboratory technologist. He has over 7 years of experience in diagnostic laboratories and has worked in various departments including microbiology, biochemistry, and hematology. He is proficient in collecting samples, operating laboratory machines, analyzing test results, and generating accurate reports. Srikanth holds a D.M.L.T degree from Vaani Institute of Medical Sciences and has worked in several diagnostic centers and hospitals in Andhra Pradesh, India.Dr. Vishnu Mittal CV by Dr. Vishnu Mittal, has 3 slides with 583 views.Dr. Vishnu Mittal has over 10 years of experience in public health. He received his Masters in Public Health from Panjab University in 2012 and his BDS from Surendra Dental College in 2009. His areas of interest include public health education, health program planning and evaluation, maternal and child health, and research. He has worked as a District Epidemiologist in Haryana and with NGOs and foundations on public health projects. His career objective is to establish a career in public health and contribute to community development and welfare.



Dr. Vishnu Mittal CVDr. Vishnu Mittal
3 slides•583 views
Dr. Vishnu Mittal has over 10 years of experience in public health. He received his Masters in Public Health from Panjab University in 2012 and his BDS from Surendra Dental College in 2009. His areas of interest include public health education, health program planning and evaluation, maternal and child health, and research. He has worked as a District Epidemiologist in Haryana and with NGOs and foundations on public health projects. His career objective is to establish a career in public health and contribute to community development and welfare.RAINBOW INSIGHTS by NARENDRA C MALHOTRA, has 68 slides with 1552 views.The document provides an overview of Rainbow Insights magazine and Rainbow Group of Hospitals. It summarizes the founding and growth of the hospital from the vision of Dr. Prabha Malhotra. The hospital has expanded to provide best services across many medical fields including IVF, neurosurgery, and more. It is dedicated to transparent, high quality patient care with compassion. The document introduces key people involved in leading and managing the hospital.



RAINBOW INSIGHTSNARENDRA C MALHOTRA
68 slides•1.6K views
The document provides an overview of Rainbow Insights magazine and Rainbow Group of Hospitals. It summarizes the founding and growth of the hospital from the vision of Dr. Prabha Malhotra. The hospital has expanded to provide best services across many medical fields including IVF, neurosurgery, and more. It is dedicated to transparent, high quality patient care with compassion. The document introduces key people involved in leading and managing the hospital.zee cv 2014 by zeeshan shaikh, has 14 slides with 445 views.This is a resume for Dr. Jeeshan G. Shaikh, an orthopedic surgeon. He received his medical education in India and obtained a diploma in orthopedics in 2005-2006. His career experience includes positions at various hospitals in Mumbai. His aims are to gain experience at a premier Mumbai institute and learn new orthopedic techniques. He provides contact information for three physician references.



zee cv 2014zeeshan shaikh
14 slides•445 views
This is a resume for Dr. Jeeshan G. Shaikh, an orthopedic surgeon. He received his medical education in India and obtained a diploma in orthopedics in 2005-2006. His career experience includes positions at various hospitals in Mumbai. His aims are to gain experience at a premier Mumbai institute and learn new orthopedic techniques. He provides contact information for three physician references.Ppscmedical medical facilities by kuljyot, has 31 slides with 502 views.The document discusses medical facilities in the Powai region. It describes the main hospitals in the area - Nahar Medical Centre located 1km from the school, and Dr. L. H. Hiranandani Hospital located 4km away. The document includes interviews with doctors at Dr. Hiranandani Hospital about common illnesses, equipment, and nursing facilities. In summary, the document examines the quality and range of healthcare available to residents of the Powai region.



Ppscmedical medical facilitieskuljyot
31 slides•502 views
The document discusses medical facilities in the Powai region. It describes the main hospitals in the area - Nahar Medical Centre located 1km from the school, and Dr. L. H. Hiranandani Hospital located 4km away. The document includes interviews with doctors at Dr. Hiranandani Hospital about common illnesses, equipment, and nursing facilities. In summary, the document examines the quality and range of healthcare available to residents of the Powai region.Textbook of Public Health Dentistry by S. S. Hiremath (z-lib.org).pdf by HubbaAli1, has 522 slides with 1624 views.CD Book, public health dentistry book , hiremath



Textbook of Public Health Dentistry by S. S. Hiremath (z-lib.org).pdfHubbaAli1
522 slides•1.6K views
CD Book, public health dentistry book , hiremathMehta's hospital profile by mehtahospitals, has 3 slides with 107 views.Dr.Mehta's Hospitals Chennai is the best hospital in Chennai with experienced doctors and trained technicians. Dr.Mehta's Hospital s one of the top hospitals in Chennai with 85 years of excellence in the medical field with successful stories of having 5000 and more happy faces cured of severe diseases.



Mehta's hospital profilemehtahospitals
3 slides•107 views
Dr.Mehta's Hospitals Chennai is the best hospital in Chennai with experienced doctors and trained technicians. Dr.Mehta's Hospital s one of the top hospitals in Chennai with 85 years of excellence in the medical field with successful stories of having 5000 and more happy faces cured of severe diseases.Resume dec,2017 by Dr. Bikha Ram Devrajani, has 2 slides with 131 views.Professor Bikha Ram Devrajani is a physician who currently serves as the Vice Chancellor of Liaquat University of Medical and Health Sciences in Jamshoro, Pakistan. He has over 28 years of clinical and teaching experience and holds medical degrees from Pakistan, the United States, and the United Kingdom. Throughout his career, Professor Devrajani has held numerous leadership roles, published over 100 research papers, and received several awards for his contributions to medicine and education.



Resume dec,2017Dr. Bikha Ram Devrajani
2 slides•131 views
Professor Bikha Ram Devrajani is a physician who currently serves as the Vice Chancellor of Liaquat University of Medical and Health Sciences in Jamshoro, Pakistan. He has over 28 years of clinical and teaching experience and holds medical degrees from Pakistan, the United States, and the United Kingdom. Throughout his career, Professor Devrajani has held numerous leadership roles, published over 100 research papers, and received several awards for his contributions to medicine and education.Fogsi focus adbhut matrutva by NARENDRA C MALHOTRA, has 161 slides with 452 views.This document discusses the launch of the "Adbhut Matrutva" project by the Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI) at the All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology on January 19th, 2018. The Adbhut Matrutva program aims to provide holistic antenatal care to reduce maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality as well as prevent noncommunicable diseases. It addresses the fetal origins of adult diseases. The document notes that the Indian government prioritizes healthcare, especially for mothers and children, through programs targeting maternal mortality, infant mortality and malnutrition.



Fogsi focus adbhut matrutvaNARENDRA C MALHOTRA
161 slides•452 views
This document discusses the launch of the "Adbhut Matrutva" project by the Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI) at the All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology on January 19th, 2018. The Adbhut Matrutva program aims to provide holistic antenatal care to reduce maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality as well as prevent noncommunicable diseases. It addresses the fetal origins of adult diseases. The document notes that the Indian government prioritizes healthcare, especially for mothers and children, through programs targeting maternal mortality, infant mortality and malnutrition.Nivedya_resume by Nivedya Amith, has 2 slides with 77 views.Dr. Nivedya D. Ramesh is a homoeopathic physician with over 2 years of experience working in multiple hospitals and clinics. She has skills in identifying patient issues, clinical examination, forming diagnoses, and prescribing homeopathic medicines. Dr. Ramesh completed her BHMS degree from Fr Muller Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital, including a 1-year internship working in 17 different medical facilities. She also has a background in psychology, having worked with cases of ADHD, depression, anxiety and stress disorders. Dr. Ramesh received several academic awards and honors during her education.



Nivedya_resumeNivedya Amith
2 slides•77 views
Dr. Nivedya D. Ramesh is a homoeopathic physician with over 2 years of experience working in multiple hospitals and clinics. She has skills in identifying patient issues, clinical examination, forming diagnoses, and prescribing homeopathic medicines. Dr. Ramesh completed her BHMS degree from Fr Muller Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital, including a 1-year internship working in 17 different medical facilities. She also has a background in psychology, having worked with cases of ADHD, depression, anxiety and stress disorders. Dr. Ramesh received several academic awards and honors during her education.resume by hafiz Ishfaq, has 16 slides with 132 views.This document contains a resume for Hafiz Muhammad Ishfaq. Some key points:
- Ishfaq is an Occupational Therapist and Senior Lecturer currently working at Helping Hands Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences in Mansehra.
- He has a B.S. in Occupational Therapy and a Master's in Public Health.
- Ishfaq has work experience in rehabilitation centers including the Pakistan Society for the Rehabilitation of Disabled in Lahore.
- He has professional certificates in areas like wrist/hand therapy and sensory integration therapy.



resumehafiz Ishfaq
16 slides•132 views
This document contains a resume for Hafiz Muhammad Ishfaq. Some key points:
- Ishfaq is an Occupational Therapist and Senior Lecturer currently working at Helping Hands Institute of Rehabilitation Sciences in Mansehra.
- He has a B.S. in Occupational Therapy and a Master's in Public Health.
- Ishfaq has work experience in rehabilitation centers including the Pakistan Society for the Rehabilitation of Disabled in Lahore.
- He has professional certificates in areas like wrist/hand therapy and sensory integration therapy.India's best of 5 recommended hospital by Merry D'souza, has 36 slides with 90 views.These hospitals are a ray of hope for those ailing patients, who want a relief from their sufferings. Hence, in this issue of Insights Success, we present to you India’s Best of 5 Recommended Hospitals, that are changing the face of healthcare through their dedication and innovation. We also recommend you read articles curated by our in-house editorial team. 



India's best of 5 recommended hospitalMerry D'souza
36 slides•90 views
These hospitals are a ray of hope for those ailing patients, who want a relief from their sufferings. Hence, in this issue of Insights Success, we present to you India’s Best of 5 Recommended Hospitals, that are changing the face of healthcare through their dedication and innovation. We also recommend you read articles curated by our in-house editorial team. CV by Rajashekar SomanattI, has 6 slides with 424 views.Dr. Rajashekar Somanatti is seeking a position in the healthcare industry. He has an MBA from the University of Northampton UK and a BDS from SDM College of Dental Sciences and Hospital. He has over 10 years of experience as a dentist and over 8 years of experience managing clinical services as an administrator at KLES Hospital. He is trained in quality management systems and risk reduction practices.



CVRajashekar SomanattI
6 slides•424 views
Dr. Rajashekar Somanatti is seeking a position in the healthcare industry. He has an MBA from the University of Northampton UK and a BDS from SDM College of Dental Sciences and Hospital. He has over 10 years of experience as a dentist and over 8 years of experience managing clinical services as an administrator at KLES Hospital. He is trained in quality management systems and risk reduction practices.Detailed report on Ramesh Hospital IN GUNTUR by madhuvenkatasainath yangalasetty, has 40 slides with 2662 views.THIS MY DETAILED REPORT ON RAMESH HOSPIAL. IN THE SUMMER INTERNSHIP TIME. IN THIS REPORT WHAT ARE AVAILABLE IN HOPITAL AND MY WORK . MY WORK WAS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ABOUT THE RAMESH HOSPITAL.



Detailed report on Ramesh Hospital IN GUNTURmadhuvenkatasainath yangalasetty
40 slides•2.7K views
THIS MY DETAILED REPORT ON RAMESH HOSPIAL. IN THE SUMMER INTERNSHIP TIME. IN THIS REPORT WHAT ARE AVAILABLE IN HOPITAL AND MY WORK . MY WORK WAS CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ABOUT THE RAMESH HOSPITAL.Cv -amit by Global Oral Health Foundation Society, has 3 slides with 78 views.Dr. Amit Saini is a dental surgeon looking to work with non-profits on oral health initiatives for underserved rural communities. He operates his own dental clinic in Nawanshahr, India and has over 20 years of experience in dentistry. He also started his own NGO called the Global Oral Health Foundation Society to provide affordable dental care to rural and marginalized groups.



Cv -amitGlobal Oral Health Foundation Society
3 slides•78 views
Dr. Amit Saini is a dental surgeon looking to work with non-profits on oral health initiatives for underserved rural communities. He operates his own dental clinic in Nawanshahr, India and has over 20 years of experience in dentistry. He also started his own NGO called the Global Oral Health Foundation Society to provide affordable dental care to rural and marginalized groups.Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1 by International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP), has 5 slides with 319 views.Dr. Ashish Pandey is a qualified dental professional with over 25 years of experience in clinical practice, teaching, and administration. He holds an MDS in Prosthodontics and an MBA in Hospital Administration. Dr. Pandey is currently the Principal, Professor, and Consultant at SDKS Dental College & Hospital in Nagpur, India. He has held various leadership roles, including Vice Principal, at other dental institutions. Dr. Pandey is skilled in prosthodontics, hospital management, teaching, and administration. He seeks an opportunity to utilize his expertise and contribute to organizational objectives through clinical work, research, and teaching.



Attachment 1424531079729 resume-1International Commision of Deplomatic Relation Human Rights & Peace (ICDRHRP)
5 slides•319 views
Recently uploaded (20)
newer Drug Delivery system by Dr Shraddha pharmacology.pptx by Dr Shraddha Mishra, has 65 slides with 57 views.novel drug delivery system , newer drug delivery system by dr shraddha mishra mbbs md pharmacology 



newer Drug Delivery system by Dr Shraddha pharmacology.pptxDr Shraddha Mishra
65 slides•57 views
novel drug delivery system , newer drug delivery system by dr shraddha mishra mbbs md pharmacology Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination by Suyash Jain, has 19 slides with 162 views.Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination
introduction about ranitidine
rise and fall of ranitidine:- drug discovery pipeline
NDMA Contamination: A Ticking Time Bomb
VALISURA laboratory
Claims by VALISURA
Testing Methods for NDMA
Regulatory Procedure Timeline
European Medical Agency
CHMP(Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use)
usfda
Recall
what are recalls
21CFR
Recall Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Regulatory actions
(FDA recall, EMA recommendations)
Guidelines to consumers
Alternatives to ranitidine
What Ranitidine Taught Us About Drug Safety?




Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA ContaminationSuyash Jain
19 slides•162 views
Ranitidine Recall:- Regulatory Response to NDMA Contamination
introduction about ranitidine
rise and fall of ranitidine:- drug discovery pipeline
NDMA Contamination: A Ticking Time Bomb
VALISURA laboratory
Claims by VALISURA
Testing Methods for NDMA
Regulatory Procedure Timeline
European Medical Agency
CHMP(Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use)
usfda
Recall
what are recalls
21CFR
Recall Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Regulatory actions
(FDA recall, EMA recommendations)
Guidelines to consumers
Alternatives to ranitidine
What Ranitidine Taught Us About Drug Safety?
Personal Protection equipments. (G).pptx by GarimaSingh204707, has 13 slides with 253 views.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to protective gear worn to prevent exposure to hazardous substances, objects, or environments. Types of PPE include head and neck protection (hard hats, safety helmets), eye and face protection (safety glasses, goggles), hearing protection (earplugs, earmuffs), respiratory protection (respirators, masks), hand and arm protection (gloves, sleeves), body protection (lab coats, coveralls), and foot and leg protection (safety shoes, boots). PPE is designed to prevent injuries and illnesses in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and healthcare.



Personal Protection equipments. (G).pptxGarimaSingh204707
13 slides•253 views
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) refers to protective gear worn to prevent exposure to hazardous substances, objects, or environments. Types of PPE include head and neck protection (hard hats, safety helmets), eye and face protection (safety glasses, goggles), hearing protection (earplugs, earmuffs), respiratory protection (respirators, masks), hand and arm protection (gloves, sleeves), body protection (lab coats, coveralls), and foot and leg protection (safety shoes, boots). PPE is designed to prevent injuries and illnesses in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and healthcare.. Introduction to Suspension therapy.pptx by Dr. Prashant Kaushik, has 28 slides with 45 views.Contents: -Definition, Principle, Advantages, Suspension instruments, Procedure, Types of suspension, Techniques.
Definition: - It is defined as suspending a part of the body or whole body with the supported slings and pulleys. That is given to the patients to increase ROM, increase muscle power, and support body part. Suspension free the body from friction of material upon the body components may be resting and it permits free movements without resistance. Late Mrs. Guthrie Smith invented the suspension apparatus.
Principle: - It is working under three principle: -
Friction.
Pendulum.
Eliminating gravity.
(a) Friction: - It occurs during a particular surface move on another. It is the force, which restrict the movement of an object. If the surface are more smooth and slippery will have less friction, in that surface the movement will be more and will cause slippery. If the surface is hard or rough results in more friction and the movements are opposed by the friction force.
The same principle is used in the suspension which has less friction causes smooth and easy movements.
(b) Pendulum: - Pendulum is heavy material suspended by the weightless thread. The force is applied on the pendulum it results in to and fro movement.
One complete swing is called as Oscillation. The arc of movement of the pendulum forms a segment of base of the cone. In the human body the pendular motion occurs mainly in the shoulder joint and the hip joint, forward leg movement and the arm swing movement while walking. The simple muscular contraction is necessary to initiate the oscillation. The same mechanism is used in the suspension therapy to maintain the muscle property, increase the range of movement and strengthening the muscles.
(c) Eliminating Gravity Movement: - If the person has the muscle power 2 (gravity eliminated movement), can go for the suspension exercises.
The patients should have minimal muscle power of 2 to under go for suspension therapy exercise. If the muscle power is above 3, the patient can go for against the gravity exercise instead of suspension therapy exercise.
Advantages: - It reduces the burden for the therapist.
Easy to lift the limbs.
Active movement can be performed easily with minimum friction.
Easier to maintain the position of limbs with slings and pulleys in the required position.
Suspension instruments: -
Suspension frame.
Supporting ropes.
Pulleys.
Slings.
S-hook and dog clips.
Wooden cleat.
(a) Suspension Frame: - It is made up of stainless steel or plastic-coated steels. In the top and head end side presents the 5-centimeter metal mesh, and the remaining sides are kept open. The measurement of the frame is 1m or 2m width X 2m length X 2m height. In the middle of the frame 2m length X 1m width X 1m height couch is placed for the patient's accommodation.
(b)Supporting Ropes: - It is 1.5 meters length, and 3 ply hemp ropes are used for the suspension to avoid slipping.




. Introduction to Suspension therapy.pptxDr. Prashant Kaushik
28 slides•45 views
Contents: -Definition, Principle, Advantages, Suspension instruments, Procedure, Types of suspension, Techniques.
Definition: - It is defined as suspending a part of the body or whole body with the supported slings and pulleys. That is given to the patients to increase ROM, increase muscle power, and support body part. Suspension free the body from friction of material upon the body components may be resting and it permits free movements without resistance. Late Mrs. Guthrie Smith invented the suspension apparatus.
Principle: - It is working under three principle: -
Friction.
Pendulum.
Eliminating gravity.
(a) Friction: - It occurs during a particular surface move on another. It is the force, which restrict the movement of an object. If the surface are more smooth and slippery will have less friction, in that surface the movement will be more and will cause slippery. If the surface is hard or rough results in more friction and the movements are opposed by the friction force.
The same principle is used in the suspension which has less friction causes smooth and easy movements.
(b) Pendulum: - Pendulum is heavy material suspended by the weightless thread. The force is applied on the pendulum it results in to and fro movement.
One complete swing is called as Oscillation. The arc of movement of the pendulum forms a segment of base of the cone. In the human body the pendular motion occurs mainly in the shoulder joint and the hip joint, forward leg movement and the arm swing movement while walking. The simple muscular contraction is necessary to initiate the oscillation. The same mechanism is used in the suspension therapy to maintain the muscle property, increase the range of movement and strengthening the muscles.
(c) Eliminating Gravity Movement: - If the person has the muscle power 2 (gravity eliminated movement), can go for the suspension exercises.
The patients should have minimal muscle power of 2 to under go for suspension therapy exercise. If the muscle power is above 3, the patient can go for against the gravity exercise instead of suspension therapy exercise.
Advantages: - It reduces the burden for the therapist.
Easy to lift the limbs.
Active movement can be performed easily with minimum friction.
Easier to maintain the position of limbs with slings and pulleys in the required position.
Suspension instruments: -
Suspension frame.
Supporting ropes.
Pulleys.
Slings.
S-hook and dog clips.
Wooden cleat.
(a) Suspension Frame: - It is made up of stainless steel or plastic-coated steels. In the top and head end side presents the 5-centimeter metal mesh, and the remaining sides are kept open. The measurement of the frame is 1m or 2m width X 2m length X 2m height. In the middle of the frame 2m length X 1m width X 1m height couch is placed for the patient's accommodation.
(b)Supporting Ropes: - It is 1.5 meters length, and 3 ply hemp ropes are used for the suspension to avoid slipping.
Post-exercise thermoregulation and associated factors by Prof. Walid Kamal, has 14 slides with 53 views.Post-exercise, especially in the heat, the body needs to restore its temperature balance. This process is complex, influenced by both thermal factors (like skin temperature) and nonthermal factors (like age, fitness, and blood pressure). These factors affect how quickly the body can lose heat and recover its core temperature. Understanding these influences is key to preventing heat strain and optimizing performance for athletes, workers, and military personnel.



Post-exercise thermoregulation and associated factorsProf. Walid Kamal
14 slides•53 views
Post-exercise, especially in the heat, the body needs to restore its temperature balance. This process is complex, influenced by both thermal factors (like skin temperature) and nonthermal factors (like age, fitness, and blood pressure). These factors affect how quickly the body can lose heat and recover its core temperature. Understanding these influences is key to preventing heat strain and optimizing performance for athletes, workers, and military personnel.PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) , H PYLORI AND GERD TREATMENT BY DR .ANKUSH GOYAL ... by Dr Ankush goyal, has 43 slides with 75 views.Comprehensive Management of Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD
I. Introduction
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are distinct yet overlapping disorders of the gastrointestinal system, marked by significant morbidity worldwide. These conditions illustrate the consequence of a disturbed harmony between offensive gastric secretions and the protective barriers of the mucosa. From ancient remedies to modern-day proton pump inhibitors and eradication therapies, the treatment approaches to these disorders represent a triumph of translational medicine.
While PUD typically involves mucosal erosion in the stomach or proximal duodenum due to Helicobacter pylori infection or NSAID use, GERD arises from the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus due to incompetent lower esophageal sphincter tone. Both conditions necessitate a thorough understanding of their etiopathogenesis for rational therapy and long-term management. This document explores the latest, evidence-based treatment paradigms, structured with clarity and clinical relevance.
---
II. Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Definition and Epidemiology
Peptic ulcers are breaks in the mucosal lining of the stomach or duodenum that penetrate the muscularis mucosa. Gastric ulcers typically occur on the lesser curvature of the stomach, while duodenal ulcers are found in the first part of the duodenum.
Globally, the prevalence of PUD has declined, largely due to H. pylori eradication, yet NSAID-related ulcers persist, especially among the elderly.
Etiology and Risk Factors
Helicobacter pylori infection – Present in ~90% of duodenal and 70% of gastric ulcers.
NSAIDs – Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, compromising mucosal defense.
Smoking – Impairs mucosal healing.
Stress (critical illness) – Leads to stress ulcers.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome – Gastrinoma with excess acid secretion.
Corticosteroids, alcohol, and genetic predisposition are other contributors.
Pathophysiology
The balance between aggressive factors (acid, pepsin, H. pylori, NSAIDs) and defensive mechanisms (mucus, bicarbonate, blood flow, prostaglandins) determines mucosal integrity.
H. pylori causes chronic inflammation and epithelial damage. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandins, reducing mucosal blood flow and bicarbonate production.
---
III. Clinical Features of Peptic Ulcer
Epigastric pain: Most common symptom; burning or gnawing in nature.
Duodenal ulcers: Pain relieved by food, occurs 2–3 hours after meals.
Gastric ulcers: Pain worsens with food intake.
Nausea, bloating, early satiety
Complications:
Bleeding: Hematemesis, melena.
Perforation: Sudden severe abdominal pain.
Gastric outlet obstruction
Penetration into adjacent organs (e.g., pancreas)
---
IV. Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer
Endoscopy: Gold standard for diagnosis and biopsy to rule out malignancy.
Rapid urease test, histology, urea breath test, stool antigen – for H. pylori.
Serologic testing (less preferred).
Barium study



PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) , H PYLORI AND GERD TREATMENT BY DR .ANKUSH GOYAL ...Dr Ankush goyal
43 slides•75 views
Comprehensive Management of Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD
I. Introduction
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are distinct yet overlapping disorders of the gastrointestinal system, marked by significant morbidity worldwide. These conditions illustrate the consequence of a disturbed harmony between offensive gastric secretions and the protective barriers of the mucosa. From ancient remedies to modern-day proton pump inhibitors and eradication therapies, the treatment approaches to these disorders represent a triumph of translational medicine.
While PUD typically involves mucosal erosion in the stomach or proximal duodenum due to Helicobacter pylori infection or NSAID use, GERD arises from the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus due to incompetent lower esophageal sphincter tone. Both conditions necessitate a thorough understanding of their etiopathogenesis for rational therapy and long-term management. This document explores the latest, evidence-based treatment paradigms, structured with clarity and clinical relevance.
---
II. Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Definition and Epidemiology
Peptic ulcers are breaks in the mucosal lining of the stomach or duodenum that penetrate the muscularis mucosa. Gastric ulcers typically occur on the lesser curvature of the stomach, while duodenal ulcers are found in the first part of the duodenum.
Globally, the prevalence of PUD has declined, largely due to H. pylori eradication, yet NSAID-related ulcers persist, especially among the elderly.
Etiology and Risk Factors
Helicobacter pylori infection – Present in ~90% of duodenal and 70% of gastric ulcers.
NSAIDs – Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, compromising mucosal defense.
Smoking – Impairs mucosal healing.
Stress (critical illness) – Leads to stress ulcers.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome – Gastrinoma with excess acid secretion.
Corticosteroids, alcohol, and genetic predisposition are other contributors.
Pathophysiology
The balance between aggressive factors (acid, pepsin, H. pylori, NSAIDs) and defensive mechanisms (mucus, bicarbonate, blood flow, prostaglandins) determines mucosal integrity.
H. pylori causes chronic inflammation and epithelial damage. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandins, reducing mucosal blood flow and bicarbonate production.
---
III. Clinical Features of Peptic Ulcer
Epigastric pain: Most common symptom; burning or gnawing in nature.
Duodenal ulcers: Pain relieved by food, occurs 2–3 hours after meals.
Gastric ulcers: Pain worsens with food intake.
Nausea, bloating, early satiety
Complications:
Bleeding: Hematemesis, melena.
Perforation: Sudden severe abdominal pain.
Gastric outlet obstruction
Penetration into adjacent organs (e.g., pancreas)
---
IV. Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer
Endoscopy: Gold standard for diagnosis and biopsy to rule out malignancy.
Rapid urease test, histology, urea breath test, stool antigen – for H. pylori.
Serologic testing (less preferred).
Barium studyPREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KAR... by KIRAN KARETHA, has 34 slides with 64 views.Premature rupture of membranes (PROM), also known as pre-labor rupture of membranes, refers to the rupture of the amniotic sac (or "water breaking") before the onset of true labor.
TYPES
Preterm premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before the 37th week of gestational age.
Term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs at or after the 37th week of pregnancy but before the onset of true labor.
3) Prolonged premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs for more than 24 hours before delivery.
4) Pre-viable pre-term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before 24 weeks of gestation. It is also known as Mid-trimester premature rupture of membrane
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
painless leakage of fluid from vagina
fetal can easily feel through belly due to loss of fluid
decrease uterine size
abdominal pain and back pain
fetal heart sound altered
gush of fluid
oligohydramnios
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
History collection (steady loss of small amount of fluid from vagina)
Sterile speculum examination: A sterile speculum examination involves using a sterile speculum, a medical instrument, to gently open the vagina for a visual examination of the cervix and vaginal walls, ensuring the speculum is sterilized before use, to prevent infection.
Pooling test: During a speculum examination, healthcare providers look for amniotic fluid accumulating in the posterior vaginal fornix (the area at the back of the vagina).
This pooling of fluid suggests that the amniotic sac has ruptured, allowing fluid to leak into the vagina.
Nitrazine test: The nitrazine test, using nitrazine paper (phenaphthazine), is a method to determine vaginal pH and detect potential amniotic fluid leakage, which can indicate a ruptured amniotic membrane, by observing a color change from yellow to blue.
Fern test: The fern test involves collecting a vaginal fluid sample, allowing it to dry on a glass slide, and then examining the dried sample under a microscope.
When amniotic fluid is present, the sodium chloride in it crystallizes, forming a characteristic fern-like pattern.
MANAGEMENT
If the patient is term > 37 weeks : Approximately 90% of patient will go into spontaneous labor within 24 hours. labor should be induced either at the time of presentation or the patient can be expected managed.
Induction of labor reduces the time of delivery and the rates of chorioamnionitis and endometritis and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.
If the patient does not go into spontaneous labor on her own then labor induction should be performed with oxytocin. So, use oxytocin or prostaglandins as indicated Otherwise, perform cesarean delivery.
COMPLICATIONS
IF FETUS REMAIN IN UTERO
Neonatal conditions
Infection and sepsis
Deformations
Umbilical cord compression
Pulmonary hypoplasia




PREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KAR...KIRAN KARETHA
34 slides•64 views
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM), also known as pre-labor rupture of membranes, refers to the rupture of the amniotic sac (or "water breaking") before the onset of true labor.
TYPES
Preterm premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before the 37th week of gestational age.
Term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs at or after the 37th week of pregnancy but before the onset of true labor.
3) Prolonged premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs for more than 24 hours before delivery.
4) Pre-viable pre-term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before 24 weeks of gestation. It is also known as Mid-trimester premature rupture of membrane
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
painless leakage of fluid from vagina
fetal can easily feel through belly due to loss of fluid
decrease uterine size
abdominal pain and back pain
fetal heart sound altered
gush of fluid
oligohydramnios
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
History collection (steady loss of small amount of fluid from vagina)
Sterile speculum examination: A sterile speculum examination involves using a sterile speculum, a medical instrument, to gently open the vagina for a visual examination of the cervix and vaginal walls, ensuring the speculum is sterilized before use, to prevent infection.
Pooling test: During a speculum examination, healthcare providers look for amniotic fluid accumulating in the posterior vaginal fornix (the area at the back of the vagina).
This pooling of fluid suggests that the amniotic sac has ruptured, allowing fluid to leak into the vagina.
Nitrazine test: The nitrazine test, using nitrazine paper (phenaphthazine), is a method to determine vaginal pH and detect potential amniotic fluid leakage, which can indicate a ruptured amniotic membrane, by observing a color change from yellow to blue.
Fern test: The fern test involves collecting a vaginal fluid sample, allowing it to dry on a glass slide, and then examining the dried sample under a microscope.
When amniotic fluid is present, the sodium chloride in it crystallizes, forming a characteristic fern-like pattern.
MANAGEMENT
If the patient is term > 37 weeks : Approximately 90% of patient will go into spontaneous labor within 24 hours. labor should be induced either at the time of presentation or the patient can be expected managed.
Induction of labor reduces the time of delivery and the rates of chorioamnionitis and endometritis and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.
If the patient does not go into spontaneous labor on her own then labor induction should be performed with oxytocin. So, use oxytocin or prostaglandins as indicated Otherwise, perform cesarean delivery.
COMPLICATIONS
IF FETUS REMAIN IN UTERO
Neonatal conditions
Infection and sepsis
Deformations
Umbilical cord compression
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Rasayan Therapy as per NCISM syllabus 25 by DrSakshi Bhardwaj, has 23 slides with 123 views.Rasayan NCISM UG syllabus 



Rasayan Therapy as per NCISM syllabus 25DrSakshi Bhardwaj
23 slides•123 views
Rasayan NCISM UG syllabus A BRIEF STUDY OF REGIONAL REPERTORY (3).pdf by sadanandarya1, has 38 slides with 49 views.Regional repertories in homeopathy are specialized reference works that focus on specific parts or systems of the body, such as the eyes, skin, respiratory system, or digestive organs. Unlike general repertories, which cover a wide range of symptoms and modalities across the entire body, regional repertories offer a more in-depth and concentrated analysis of particular areas, allowing practitioners to narrow down remedies with greater precision.
This study aims to understand the role and relevance of regional repertories in clinical practice. It explores various examples such as "Repertory of the Eyes" by William Jefferson Guernsey, and "Repertory of the Head" by J.B. Garth Wilkinson, among others. These repertories serve as valuable tools in cases where the pathology is strongly localized, and where a detailed repertorial analysis of that specific region is needed.
The study also highlights the advantages and limitations of regional repertories. While they provide focused insight and can enhance remedy selection in specific cases, they may lack the broader context required in complex or multi-systemic conditions. Thus, they are most effective when used in conjunction with general repertories and thorough case-taking.
regional repertories play a significant role in enhancing the accuracy of homeopathic prescriptions, especially in localized diseases. Their study is essential for practitioners seeking to deepen their understanding and refine their skills in remedy selection.



A BRIEF STUDY OF REGIONAL REPERTORY (3).pdfsadanandarya1
38 slides•49 views
Regional repertories in homeopathy are specialized reference works that focus on specific parts or systems of the body, such as the eyes, skin, respiratory system, or digestive organs. Unlike general repertories, which cover a wide range of symptoms and modalities across the entire body, regional repertories offer a more in-depth and concentrated analysis of particular areas, allowing practitioners to narrow down remedies with greater precision.
This study aims to understand the role and relevance of regional repertories in clinical practice. It explores various examples such as "Repertory of the Eyes" by William Jefferson Guernsey, and "Repertory of the Head" by J.B. Garth Wilkinson, among others. These repertories serve as valuable tools in cases where the pathology is strongly localized, and where a detailed repertorial analysis of that specific region is needed.
The study also highlights the advantages and limitations of regional repertories. While they provide focused insight and can enhance remedy selection in specific cases, they may lack the broader context required in complex or multi-systemic conditions. Thus, they are most effective when used in conjunction with general repertories and thorough case-taking.
regional repertories play a significant role in enhancing the accuracy of homeopathic prescriptions, especially in localized diseases. Their study is essential for practitioners seeking to deepen their understanding and refine their skills in remedy selection.Abdominal Pain-Allquadrants-casebasedlearning.pdf by Selvaraj Balasubramani, has 89 slides with 52 views.This is a case based teaching abdominal pain PPTs



Abdominal Pain-Allquadrants-casebasedlearning.pdfSelvaraj Balasubramani
89 slides•52 views
This is a case based teaching abdominal pain PPTsArts-In-Medicine cancer support presentation .pptx by JessShirley3, has 24 slides with 19 views.Arts-In-Medicine cancer support presentation 



Arts-In-Medicine cancer support presentation .pptxJessShirley3
24 slides•19 views
Arts-In-Medicine cancer support presentation Emergency Studies in Nuclear Medicine .pdf by MiadAlsulami, has 32 slides with 241 views.This lecture can serve as a bullet-point review of the emergency studies in nuclear medicine. The outline is as follows:
- Pulmonary Embolism.
- GI Bleeding.
- ATN.
- Shunt Patency.
- Brain Death.



Emergency Studies in Nuclear Medicine .pdfMiadAlsulami
32 slides•241 views
This lecture can serve as a bullet-point review of the emergency studies in nuclear medicine. The outline is as follows:
- Pulmonary Embolism.
- GI Bleeding.
- ATN.
- Shunt Patency.
- Brain Death.Liver - Surgical Anatomy, Abscess and Liver - Tumours by Uthamalingam Murali, has 59 slides with 149 views.This PPT includes - two topics - Liver abscess & Liver timours which is very much essential for MBBS - Students. The students should know the causes, clinical features & management aspects of the above liver diseases. Also it includes the latest staging system of liver tumours. 



Liver - Surgical Anatomy, Abscess and Liver - TumoursUthamalingam Murali
59 slides•149 views
This PPT includes - two topics - Liver abscess & Liver timours which is very much essential for MBBS - Students. The students should know the causes, clinical features & management aspects of the above liver diseases. Also it includes the latest staging system of liver tumours. recent HIV/AIDS drugs and pharmacology by Dr Shraddha.pptx by Dr Shraddha Mishra, has 58 slides with 59 views.pharmacology of HIV drugs , recent advances in hiv drugs
AIDS drugs 



recent HIV/AIDS drugs and pharmacology by Dr Shraddha.pptxDr Shraddha Mishra
58 slides•59 views
pharmacology of HIV drugs , recent advances in hiv drugs
AIDS drugs Autocoids mcq.ankush goyal gmc patiala punjab by Dr Ankush goyal, has 54 slides with 276 views.Lipid Autocoids: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Lipid autocoids, also known as eicosanoids and related lipid mediators, are bioactive molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). These molecules play crucial roles in inflammation, immunity, hemostasis, cardiovascular function, and various physiological and pathological processes. Unlike classical hormones, lipid autocoids act locally, exerting their effects at or near their site of synthesis.
This document provides an in-depth analysis of lipid autocoids, covering their biosynthesis, classification, physiological roles, and clinical significance.
Classification of Lipid Autocoids
Lipid autocoids are broadly classified into the following categories:
1. Eicosanoids (Derived from Arachidonic Acid)
Prostaglandins (PGs)
Thromboxanes (TXs)
Leukotrienes (LTs)
Lipoxins (LXs)
2. Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators (SPMs)
Resolvins
Protectins
Maresins
3. Endocannabinoids
Anandamide (AEA)
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
4. Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF)
5. Sphingolipid-Derived Mediators
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P)
Ceramides
Biosynthesis of Lipid Autocoids
Lipid autocoids are derived from membrane phospholipids through enzymatic pathways:
1. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Activation:
PLA2 catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid (AA) from membrane phospholipids.
2. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Pathway:
Converts AA into prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
COX-1: Constitutive enzyme (housekeeping functions).
COX-2: Inducible enzyme (inflammation and pain response).
3. Lipoxygenase (LOX) Pathway:
Converts AA into leukotrienes and lipoxins.
5-LOX: Leads to leukotrienes (inflammation, bronchoconstriction).
12-LOX & 15-LOX: Lead to lipoxins (anti-inflammatory action).
4. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Pathway:
Converts AA into epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which regulate vascular tone.
5. Endocannabinoid Biosynthesis:
Derived from membrane phospholipids via enzymatic reactions.
Degraded by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).
Physiological Roles of Lipid Autocoids
1. Inflammation and Immune Response
Prostaglandins (e.g., PGE2) modulate fever and pain.
Leukotrienes mediate allergic responses and asthma.
Lipoxins and resolvins promote resolution of inflammation.
2. Cardiovascular System
Thromboxanes (TXA2) induce platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction.
Prostacyclin (PGI2) inhibits platelet aggregation and promotes vasodilation.
EETs regulate blood pressure and vascular homeostasis.
3. Pulmonary Function
Leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) are potent bronchoconstrictors.
PGE2 has bronchodilatory effects.
4. Renal Function
Prostaglandins regulate glomerular filtration rate and sodium excretion.
EETs contribute to natriuresis.
5. Neurotransmission and Pain
Endocannabinoids modulate pain perception and neuroprotection.
Prostaglandins contribute to central pain sensitization.
6. Reproductive System
P



Autocoids mcq.ankush goyal gmc patiala punjabDr Ankush goyal
54 slides•276 views
Lipid Autocoids: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Lipid autocoids, also known as eicosanoids and related lipid mediators, are bioactive molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). These molecules play crucial roles in inflammation, immunity, hemostasis, cardiovascular function, and various physiological and pathological processes. Unlike classical hormones, lipid autocoids act locally, exerting their effects at or near their site of synthesis.
This document provides an in-depth analysis of lipid autocoids, covering their biosynthesis, classification, physiological roles, and clinical significance.
Classification of Lipid Autocoids
Lipid autocoids are broadly classified into the following categories:
1. Eicosanoids (Derived from Arachidonic Acid)
Prostaglandins (PGs)
Thromboxanes (TXs)
Leukotrienes (LTs)
Lipoxins (LXs)
2. Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators (SPMs)
Resolvins
Protectins
Maresins
3. Endocannabinoids
Anandamide (AEA)
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
4. Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF)
5. Sphingolipid-Derived Mediators
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P)
Ceramides
Biosynthesis of Lipid Autocoids
Lipid autocoids are derived from membrane phospholipids through enzymatic pathways:
1. Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) Activation:
PLA2 catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid (AA) from membrane phospholipids.
2. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Pathway:
Converts AA into prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
COX-1: Constitutive enzyme (housekeeping functions).
COX-2: Inducible enzyme (inflammation and pain response).
3. Lipoxygenase (LOX) Pathway:
Converts AA into leukotrienes and lipoxins.
5-LOX: Leads to leukotrienes (inflammation, bronchoconstriction).
12-LOX & 15-LOX: Lead to lipoxins (anti-inflammatory action).
4. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Pathway:
Converts AA into epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which regulate vascular tone.
5. Endocannabinoid Biosynthesis:
Derived from membrane phospholipids via enzymatic reactions.
Degraded by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).
Physiological Roles of Lipid Autocoids
1. Inflammation and Immune Response
Prostaglandins (e.g., PGE2) modulate fever and pain.
Leukotrienes mediate allergic responses and asthma.
Lipoxins and resolvins promote resolution of inflammation.
2. Cardiovascular System
Thromboxanes (TXA2) induce platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction.
Prostacyclin (PGI2) inhibits platelet aggregation and promotes vasodilation.
EETs regulate blood pressure and vascular homeostasis.
3. Pulmonary Function
Leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) are potent bronchoconstrictors.
PGE2 has bronchodilatory effects.
4. Renal Function
Prostaglandins regulate glomerular filtration rate and sodium excretion.
EETs contribute to natriuresis.
5. Neurotransmission and Pain
Endocannabinoids modulate pain perception and neuroprotection.
Prostaglandins contribute to central pain sensitization.
6. Reproductive System
PDesigning for Menopause: How to Design with Empathy for People in Transition by 1508 A/S, has 76 slides with 25 views.In this Morgenbooster, we will share our process in designing with empathy – an essential element of the 1508 DNA.



Designing for Menopause: How to Design with Empathy for People in Transition1508 A/S
76 slides•25 views
In this Morgenbooster, we will share our process in designing with empathy – an essential element of the 1508 DNA.#BRAINWAVE LEARNING pdf by #SM - #Sujitha #mohitha (doctor of pharmacy 💊) #ph... by Mohithakumaran , has 16 slides with 43 views.In this Depression we described about
Definition
Types
Etiology
Epidemiology
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Diagnosis
Treatment 



#BRAINWAVE LEARNING pdf by #SM - #Sujitha #mohitha (doctor of pharmacy 💊) #ph...Mohithakumaran
16 slides•43 views
In this Depression we described about
Definition
Types
Etiology
Epidemiology
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Diagnosis
Treatment disorder of parathyroid gland Hyperparathyroidism and Hypoparathyroidism by Khushbu Arya, has 70 slides with 14 views.Disorder of Parathyroid Gland
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is hypersecretion of PTH.
Classification
Hyperthyroidism is classified in to two
1. Primary hyperparathyroidism.
2. Secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is a relatively common disorder, affecting approximately 2% of the population over 55 years of age.
• It most commonly affects post-menopausal women, with women having a 2 to 3 times greater risk of developing primary hyperparathyroidism than men.
Cause:
It typically results from a single adenoma, but may also result from multiple adenomas, hypertrophy of the parathyroid glands, carcinoma, radiation to the neck, lithium use.
Hereditary factors: such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) types I and II.
The autonomous hypersecretion of PTH in primary hyperparathyroidism results in hypercalcemia, which, together with elevated or sometimes normal PTH levels without an underlying stimulus is diagnostic for this disease.
Other common causes of hypercalcemia, such as cancer, would result in depressed PTH levels.
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually incidentally found in the early stages of the disease on routine bloodwork, demonstrating an increased serum calcium level.
• Most patients are asymptomatic at diagnosis or have non-specific symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, mental fogginess, anxiety, depression, gastroesophageal reflux, or bone pains. Patients who present at later stages may have symptomatic hypercalcemia with severe bone disease, nephrolithiasis, neuromuscular dysfunction, gastrointestinal problems, or cardiovascular disease.
• Rarely, a volume-depleted patient with primary hyperparathyroidism may present in hypercalcaemic crisis secondary to a rapid spike in serum calcium level that may lead to dangerous cardio and neurotoxicity, renal impairment, and gastrointestinal dysfunction
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
• Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, which is characterized by inappropriate secretion of PTH, secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs as an appropriate reaction to a stimulus that induces the secretion of PTH from the parathyroid glands.
• In secondary hyperparathyroidism, PTH is synthesized and secreted in response to chronically low serum calcium levels, which may result from malabsorption of calcium from the GI tract, vitamin D deficiency, renal insufficiency, or medications such as thiazide diuretics.
• On bloodwork, this would appear as a low to normal serum calcium level with an elevated PTH level; this differentiates secondary from tertiary hyperparathyroidism, which results when secondary hyperparathyroidism progresses, and the parathyroid become overwhelmed and start producing PTH semi-autonomously without proper stimulation.
• When this occurs, hypercalcemia ensues, and bloodwork results appear similar to those with primary hyperparathyroidism.
• The difference between primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism is that tertiarHypoparat



disorder of parathyroid gland Hyperparathyroidism and HypoparathyroidismKhushbu Arya
70 slides•14 views
Disorder of Parathyroid Gland
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is hypersecretion of PTH.
Classification
Hyperthyroidism is classified in to two
1. Primary hyperparathyroidism.
2. Secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is a relatively common disorder, affecting approximately 2% of the population over 55 years of age.
• It most commonly affects post-menopausal women, with women having a 2 to 3 times greater risk of developing primary hyperparathyroidism than men.
Cause:
It typically results from a single adenoma, but may also result from multiple adenomas, hypertrophy of the parathyroid glands, carcinoma, radiation to the neck, lithium use.
Hereditary factors: such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) types I and II.
The autonomous hypersecretion of PTH in primary hyperparathyroidism results in hypercalcemia, which, together with elevated or sometimes normal PTH levels without an underlying stimulus is diagnostic for this disease.
Other common causes of hypercalcemia, such as cancer, would result in depressed PTH levels.
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually incidentally found in the early stages of the disease on routine bloodwork, demonstrating an increased serum calcium level.
• Most patients are asymptomatic at diagnosis or have non-specific symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, mental fogginess, anxiety, depression, gastroesophageal reflux, or bone pains. Patients who present at later stages may have symptomatic hypercalcemia with severe bone disease, nephrolithiasis, neuromuscular dysfunction, gastrointestinal problems, or cardiovascular disease.
• Rarely, a volume-depleted patient with primary hyperparathyroidism may present in hypercalcaemic crisis secondary to a rapid spike in serum calcium level that may lead to dangerous cardio and neurotoxicity, renal impairment, and gastrointestinal dysfunction
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
• Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, which is characterized by inappropriate secretion of PTH, secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs as an appropriate reaction to a stimulus that induces the secretion of PTH from the parathyroid glands.
• In secondary hyperparathyroidism, PTH is synthesized and secreted in response to chronically low serum calcium levels, which may result from malabsorption of calcium from the GI tract, vitamin D deficiency, renal insufficiency, or medications such as thiazide diuretics.
• On bloodwork, this would appear as a low to normal serum calcium level with an elevated PTH level; this differentiates secondary from tertiary hyperparathyroidism, which results when secondary hyperparathyroidism progresses, and the parathyroid become overwhelmed and start producing PTH semi-autonomously without proper stimulation.
• When this occurs, hypercalcemia ensues, and bloodwork results appear similar to those with primary hyperparathyroidism.
• The difference between primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism is that tertiarHypoparatNeurotransmitters by dr k ambareesha PhD by Dr K Ambareesha Goud PhD, has 22 slides with 164 views.Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells (neurons) and other cells, playing a crucial role in various bodily functions, including motor control, perception, and cognitive processes



Neurotransmitters by dr k ambareesha PhDDr K Ambareesha Goud PhD
22 slides•164 views
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells (neurons) and other cells, playing a crucial role in various bodily functions, including motor control, perception, and cognitive processesPEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) , H PYLORI AND GERD TREATMENT BY DR .ANKUSH GOYAL ... by Dr Ankush goyal, has 43 slides with 75 views.Comprehensive Management of Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD
I. Introduction
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are distinct yet overlapping disorders of the gastrointestinal system, marked by significant morbidity worldwide. These conditions illustrate the consequence of a disturbed harmony between offensive gastric secretions and the protective barriers of the mucosa. From ancient remedies to modern-day proton pump inhibitors and eradication therapies, the treatment approaches to these disorders represent a triumph of translational medicine.
While PUD typically involves mucosal erosion in the stomach or proximal duodenum due to Helicobacter pylori infection or NSAID use, GERD arises from the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus due to incompetent lower esophageal sphincter tone. Both conditions necessitate a thorough understanding of their etiopathogenesis for rational therapy and long-term management. This document explores the latest, evidence-based treatment paradigms, structured with clarity and clinical relevance.
---
II. Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Definition and Epidemiology
Peptic ulcers are breaks in the mucosal lining of the stomach or duodenum that penetrate the muscularis mucosa. Gastric ulcers typically occur on the lesser curvature of the stomach, while duodenal ulcers are found in the first part of the duodenum.
Globally, the prevalence of PUD has declined, largely due to H. pylori eradication, yet NSAID-related ulcers persist, especially among the elderly.
Etiology and Risk Factors
Helicobacter pylori infection – Present in ~90% of duodenal and 70% of gastric ulcers.
NSAIDs – Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, compromising mucosal defense.
Smoking – Impairs mucosal healing.
Stress (critical illness) – Leads to stress ulcers.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome – Gastrinoma with excess acid secretion.
Corticosteroids, alcohol, and genetic predisposition are other contributors.
Pathophysiology
The balance between aggressive factors (acid, pepsin, H. pylori, NSAIDs) and defensive mechanisms (mucus, bicarbonate, blood flow, prostaglandins) determines mucosal integrity.
H. pylori causes chronic inflammation and epithelial damage. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandins, reducing mucosal blood flow and bicarbonate production.
---
III. Clinical Features of Peptic Ulcer
Epigastric pain: Most common symptom; burning or gnawing in nature.
Duodenal ulcers: Pain relieved by food, occurs 2–3 hours after meals.
Gastric ulcers: Pain worsens with food intake.
Nausea, bloating, early satiety
Complications:
Bleeding: Hematemesis, melena.
Perforation: Sudden severe abdominal pain.
Gastric outlet obstruction
Penetration into adjacent organs (e.g., pancreas)
---
IV. Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer
Endoscopy: Gold standard for diagnosis and biopsy to rule out malignancy.
Rapid urease test, histology, urea breath test, stool antigen – for H. pylori.
Serologic testing (less preferred).
Barium study



PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) , H PYLORI AND GERD TREATMENT BY DR .ANKUSH GOYAL ...Dr Ankush goyal
43 slides•75 views
PREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KAR... by KIRAN KARETHA, has 34 slides with 64 views.Premature rupture of membranes (PROM), also known as pre-labor rupture of membranes, refers to the rupture of the amniotic sac (or "water breaking") before the onset of true labor.
TYPES
Preterm premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before the 37th week of gestational age.
Term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs at or after the 37th week of pregnancy but before the onset of true labor.
3) Prolonged premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs for more than 24 hours before delivery.
4) Pre-viable pre-term premature rupture of membrane: when rupture of membranes occurs before 24 weeks of gestation. It is also known as Mid-trimester premature rupture of membrane
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
painless leakage of fluid from vagina
fetal can easily feel through belly due to loss of fluid
decrease uterine size
abdominal pain and back pain
fetal heart sound altered
gush of fluid
oligohydramnios
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
History collection (steady loss of small amount of fluid from vagina)
Sterile speculum examination: A sterile speculum examination involves using a sterile speculum, a medical instrument, to gently open the vagina for a visual examination of the cervix and vaginal walls, ensuring the speculum is sterilized before use, to prevent infection.
Pooling test: During a speculum examination, healthcare providers look for amniotic fluid accumulating in the posterior vaginal fornix (the area at the back of the vagina).
This pooling of fluid suggests that the amniotic sac has ruptured, allowing fluid to leak into the vagina.
Nitrazine test: The nitrazine test, using nitrazine paper (phenaphthazine), is a method to determine vaginal pH and detect potential amniotic fluid leakage, which can indicate a ruptured amniotic membrane, by observing a color change from yellow to blue.
Fern test: The fern test involves collecting a vaginal fluid sample, allowing it to dry on a glass slide, and then examining the dried sample under a microscope.
When amniotic fluid is present, the sodium chloride in it crystallizes, forming a characteristic fern-like pattern.
MANAGEMENT
If the patient is term > 37 weeks : Approximately 90% of patient will go into spontaneous labor within 24 hours. labor should be induced either at the time of presentation or the patient can be expected managed.
Induction of labor reduces the time of delivery and the rates of chorioamnionitis and endometritis and admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.
If the patient does not go into spontaneous labor on her own then labor induction should be performed with oxytocin. So, use oxytocin or prostaglandins as indicated Otherwise, perform cesarean delivery.
COMPLICATIONS
IF FETUS REMAIN IN UTERO
Neonatal conditions
Infection and sepsis
Deformations
Umbilical cord compression
Pulmonary hypoplasia




PREMATURE RUPTURE OF MEMBRANES.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KAR...KIRAN KARETHA
34 slides•64 views
Designing for Menopause: How to Design with Empathy for People in Transition by 1508 A/S, has 76 slides with 25 views.In this Morgenbooster, we will share our process in designing with empathy – an essential element of the 1508 DNA.



Designing for Menopause: How to Design with Empathy for People in Transition1508 A/S
76 slides•25 views
#BRAINWAVE LEARNING pdf by #SM - #Sujitha #mohitha (doctor of pharmacy 💊) #ph... by Mohithakumaran , has 16 slides with 43 views.In this Depression we described about
Definition
Types
Etiology
Epidemiology
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Diagnosis
Treatment 



#BRAINWAVE LEARNING pdf by #SM - #Sujitha #mohitha (doctor of pharmacy 💊) #ph...Mohithakumaran
16 slides•43 views
disorder of parathyroid gland Hyperparathyroidism and Hypoparathyroidism by Khushbu Arya, has 70 slides with 14 views.Disorder of Parathyroid Gland
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is hypersecretion of PTH.
Classification
Hyperthyroidism is classified in to two
1. Primary hyperparathyroidism.
2. Secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is a relatively common disorder, affecting approximately 2% of the population over 55 years of age.
• It most commonly affects post-menopausal women, with women having a 2 to 3 times greater risk of developing primary hyperparathyroidism than men.
Cause:
It typically results from a single adenoma, but may also result from multiple adenomas, hypertrophy of the parathyroid glands, carcinoma, radiation to the neck, lithium use.
Hereditary factors: such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) types I and II.
The autonomous hypersecretion of PTH in primary hyperparathyroidism results in hypercalcemia, which, together with elevated or sometimes normal PTH levels without an underlying stimulus is diagnostic for this disease.
Other common causes of hypercalcemia, such as cancer, would result in depressed PTH levels.
• Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually incidentally found in the early stages of the disease on routine bloodwork, demonstrating an increased serum calcium level.
• Most patients are asymptomatic at diagnosis or have non-specific symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, mental fogginess, anxiety, depression, gastroesophageal reflux, or bone pains. Patients who present at later stages may have symptomatic hypercalcemia with severe bone disease, nephrolithiasis, neuromuscular dysfunction, gastrointestinal problems, or cardiovascular disease.
• Rarely, a volume-depleted patient with primary hyperparathyroidism may present in hypercalcaemic crisis secondary to a rapid spike in serum calcium level that may lead to dangerous cardio and neurotoxicity, renal impairment, and gastrointestinal dysfunction
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
• Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, which is characterized by inappropriate secretion of PTH, secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs as an appropriate reaction to a stimulus that induces the secretion of PTH from the parathyroid glands.
• In secondary hyperparathyroidism, PTH is synthesized and secreted in response to chronically low serum calcium levels, which may result from malabsorption of calcium from the GI tract, vitamin D deficiency, renal insufficiency, or medications such as thiazide diuretics.
• On bloodwork, this would appear as a low to normal serum calcium level with an elevated PTH level; this differentiates secondary from tertiary hyperparathyroidism, which results when secondary hyperparathyroidism progresses, and the parathyroid become overwhelmed and start producing PTH semi-autonomously without proper stimulation.
• When this occurs, hypercalcemia ensues, and bloodwork results appear similar to those with primary hyperparathyroidism.
• The difference between primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism is that tertiarHypoparat



disorder of parathyroid gland Hyperparathyroidism and HypoparathyroidismKhushbu Arya
70 slides•14 views
DR MANISH-2.pdf laser proctology piles and fistula
- 1. D R M A N I S H RAJPUT ht t ps://dr manishr ajput .com Bookan appointment!
- 2. IN T R O D U C T IO N Dr . Manish Rajput is an I nterventional Radiologist & Team Lead, Team I R Jaipur . They are the biggest team of I nterventional Radiologists. They are trained from Tata Memorial Center , Mumbai, I ndia. They have worked in so many government and corporate hospitals across the country.
- 3. Medical school (MBBS):2005-2011: -People’s Medical College, Bhopal(MP) DNB (Radio diagnosis): - Apollo hospital, Hyderabad(Telangana) FVIR (PDCC):- Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai(Maharashtra) Senior Resident: Hinduja Hospital Mumbai, SMS Hospital Jaipur Past Visiting Doctor:Leelavati Hospital Mumbai, Breach Candy Hospital Mumbai, Wockhardt Hospital Mumbai, Hinduja Hospital Mumbai Ex Assitant Professor:JNU Medical College, Jaipur Currently Working as Senior Consultant Interventional Radiologist in various corporate hospitals of Rajasthan based in Jaipur HIS EDUCATION
- 4. S T R E N G T H S Ilead the biggest I R team in the state. Vast portfolio for I R services. All the team members are from Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Extensive experience in performing and interpreting basic Radio-Diagnosis. Gained experience in performing I nterventional Radiologic procedures. Ipossess oratory skill by speaking at numerous industry events. Ability to teach complex concepts in a basic manner .
- 5. Varicose Veins Prostate Artery Embolization PRG Biopsy and fNAC Angioplasty & Venoplasty PCN & DJ Stenting O U R S E R V I C E S
- 6. +91 7729021111 dr.manish@infinityintervention.com O-5-A, Adinath Marg, Near Surya Hospital, C Scheme, Ashok Nagar, Jaipur, Rajasthan 302001 C ON TA C T US!
